Global Banking Outlook 2026: Comprehensive strategic summary & action plan
The global banking sector enters 2026 operating under conditions characterized by three defining forces: divergent monetary policy, the confluence of regulatory mandates, the imperative of AI industrialization. The strategic mandate is clear: transform technology, culture, and operations simultaneously. Diversify revenue through fee-based services, optimize costs via AI and branch rationalization, compete and cooperate strategically with fintechs, and maintain regulatory excellence across all jurisdictions.

The global banking sector enters 2026 operating under conditions characterized by three defining forces:
1) Divergent monetary policy creating distinct regional profitability challenges;
2) The confluence of regulatory mandates compelling simultaneous execution of Basel III/IV capital finalization and mandatory climate risk integration; and
3) The imperative of AI industrialization requiring foundational data infrastructure transformation.
These forces intersect with mobile-first disruption, evolving branch economics, cultural transformation needs, and intensifying fintech competition.
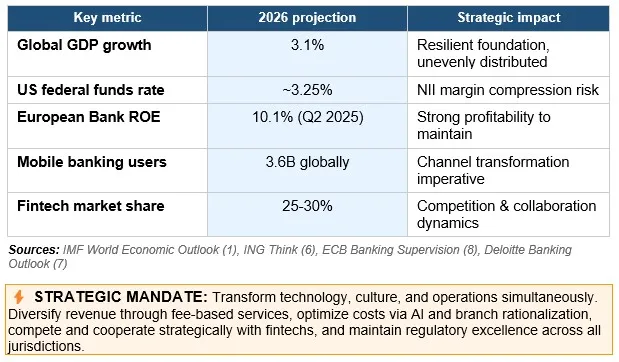
Global growth is projected at 3.1%, yet regional financial conditions are decoupling dramatically.
This divergence demands that CFOs and CSOs urgently pivot strategies toward robust non-interest income streams, especially in jurisdictions facing margin compression.
The strategic mandate is clear: Capital must be efficiently deployed to[L1] [ÖT2]
• modernize core data infrastructure
• comply with converging regulations
• scale AI from pilots to enterprise-wide drivers
• optimize branch networks
• transform organizational culture
• compete and cooperate effectively with fintechs while maintaining profitability.
Regional economic landscape & divergence
Banking conditions vary dramatically by region, requiring tailored strategies while maintaining global operational coherence. Growth is unevenly distributed, disproportionately favoring advanced economies and digitally ready sectors.
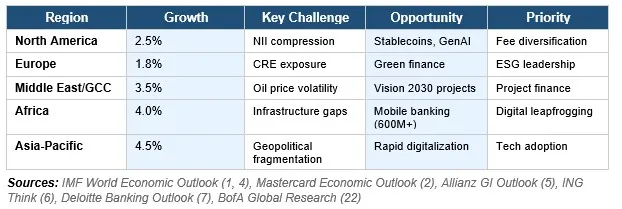
Geopolitical fragmentation is rewiring globalization, particularly impacting high-technology goods trade. Banks must adapt credit and operational risk models for complex, asymmetric trade patterns while strengthening KYC protocols and counterparty risk evaluation tied to supply chain resilience indicators.
Regulatory convergence: the compliance marathon
2026 represents a pivotal inflection point with Basel III/IV finalization, mandatory climate risk integration, cybersecurity frameworks, AML modernization, and digital accessibility mandates converging simultaneously across all major jurisdictions.
Basel III/IV implementation
US implementation was proposed to begin in July 2025 with staggered rollout through July 2028; however, final rules have not yet been published as of December 2025.
European CRR3, effective January 2025, mandates a 72.5% output floor that phases in gradually: 50% (2025) → 55% (2026) → 60% (2027) → 65% (2028) → 70% (2029) → 72.5% (2030), with transitional cap limiting year-over-year RWA increases to 25%.
US estimates indicate 16% aggregate CET1 capital increase for affected institutions.
APAC faces varied timelines—Canada completed implementation in 2023-2024, while Singapore, Australia, and Hong Kong follow through 2025-2026.
The immediate implication for CSOs is data integrity—institutions addressing poor data quality in fragmented legacy systems can significantly mitigate capital impact.
Investment in data lineage, accuracy, and integrity must be viewed as direct capital optimization strategy, with dual calculations required for floored and unfloored RWA at all consolidation levels.
Climate risk & ESG integration
EBA guidelines on ESG risk management will become applicable January 11, 2026 (January 11, 2027 for small/non-complex institutions), requiring systematic integration of physical risks (climate events, natural disasters) and transition risks (technological obsolescence, capital reallocation, policy changes) into governance, risk management, strategic planning, ICAAP, and ILAAP.
Requirements include annual materiality assessments with minimum 10-year horizons and transition plans aligned with EU 2050 climate neutrality.
China mandates sustainability reports by April 30, 2026, for 400-450+ companies including major banks (SSE 180, STAR 50, SZSE 100, ChiNext indices), covering governance, strategy, risk management, and metrics including mandatory scope 1 & 2 emissions.
CSOs must immediately integrate climate scenario analysis with traditional credit risk modeling, as transition risks now directly impact credit quality of carbon-intensive portfolios.
Critical actions include carbon intensity tracking by sector, transition risk scoring for high-emission exposures, and ESG data collection frameworks covering GHG emissions, energy consumption, and client transition plans.
Cybersecurity & operational resilience
The EU Cyber Resilience Act (entered into force December 10, 2024; reporting obligations September 11, 2026; full application December 11, 2027) introduces mandatory cybersecurity requirements for digital products, requiring software bill of materials (SBOM), 24-hour vulnerability notifications, 72-hour follow-up reports, and 14-day final corrective reports.
C-level executives must audit technology providers for SBOM documentation, security update mechanisms, vulnerability disclosure processes, and incident response capabilities, expanding third-party risk management beyond traditional contract checks.
Complementary frameworks include NIS 2 Directive (member state implementation October 17, 2024) and DORA (Digital Operational Resilience Act, effective January 17, 2025) establishing ICT risk management and third-party oversight for financial entities.
Anti-money laundering & financial crime compliance
FinCEN's Investment Adviser AML Rule, delayed from January 1, 2026, to January 1, 2028, will require SEC-registered investment advisers to implement AML/CFT programs and file Suspicious Activity Reports.
The Real Estate Professional AML Rule took effect December 1, 2025. Community Bank BSA/AML Procedures (effective February 1, 2026) will reduce burden for low-risk institutions.
FinCEN priorities focus on national security threats (sanctions violations, cartel financing), complex money laundering including Chinese money laundering organizations, and digital asset compliance through enhanced Travel Rule enforcement for virtual asset service providers.
The EU Anti-Money Laundering Authority (AMLA), operational since 2024, is expected to issue technical standards on sanctions by July 10, 2026. 6AMLD imposes stricter penalties, mandates centralized beneficial ownership registries, and enhances cross-border cooperation.
China's AML Law amendments (April 2024 draft) propose expanded requirements and increased penalties.
Financial institutions must deploy AI-powered transaction monitoring, blockchain analytics, real-time beneficial ownership verification, and automated sanctions screening with board-level oversight and cross-jurisdictional coordination.
Digital accessibility compliance
In the US, the ADA Title II digital accessibility rule requires all web content and mobile applications to meet WCAG 2.1 Level AA standards by April 24, 2026 for large entities (serving 50,000+ population) and April 26, 2027 for smaller entities.
Financial institutions face additional obligations under ADA Title III (banks as public accommodations) and Section 504 (federal fund recipients), with courts increasingly interpreting these to include digital services.
WCAG 2.1 AA requirements mandate perceivable content (text alternatives, captions, 4.5:1 color contrast), operable interfaces (full keyboard navigation), understandable design (clear labels, error identification), and robust compatibility with assistive technologies.
Compliance scope includes online banking platforms, mobile applications, websites, PDF documents, and ATM interfaces.
Major banks have paid $1M+ settlements for accessibility violations. Implementation requires comprehensive audits (automated tools miss 60-70% of issues), critical barrier remediation focusing on forms, navigation, and color contrast, and accessibility policies including vendor procurement requirements. Initial remediation costs range $50K-$500K+ with $20K-$100K annual monitoring, but ROI includes lawsuit prevention and market expansion to 61 million Americans with disabilities.
Integrated compliance framework
Convergence requires centralized coordination through enterprise compliance committees with cross-functional authority managing Basel/capital, climate/ESG, cyber/tech, AML/financial crime, and accessibility workstreams.
Unified data infrastructure serving Basel RWA calculations, climate stress testing, cyber monitoring, AML surveillance, and accessibility tracking reduces redundant costs by 30-40%.
Technology stack priorities include regtech platforms, AI/ML analytics, cloud infrastructure, API integration, and automated monitoring dashboards. Non-compliance risks: $1M-$100M+ penalties, capital add-ons, reputational damage, litigation costs, and market restrictions.

AI industrialization: Beyond pilot purgatory
The competitive advantage in 2026-2028 belongs to institutions achieving AI industrialization—moving from isolated pilots to enterprise-wide operational transformation. Generative AI presents substantial opportunity particularly in investment banking, with forecasts suggesting top 14 global banks could boost front-office productivity by 27-35%, translating to $3.5 million additional revenue per front-office employee.
High-impact applications
• Investment banking: Deal analysis, pitch preparation, market research
• Compliance and risk management: Enhanced AML and fraud detection, real-time credit monitoring, predictive portfolio analytics
• Customer service: Intelligent chatbots, personalized advice, 24/7 support
• Operations: Compliance monitoring automation, document processing, reconciliation
Data infrastructure imperative
AI success depends entirely on data quality and accessibility. Most banks struggle with fragmented data across legacy systems, inconsistent governance, and insufficient metadata. Without addressing these foundations, AI initiatives remain trapped in pilot phase. The goal for 2027 is creating "AI-ready data"—accurate, timely, broad, and securely governed—supporting breakthrough agentic AI applications that perform complex, multi-step tasks autonomously. Poor data infrastructure causes models to stall or produce hallucinations, posing significant operational and reputational risks.

Mobile banking revolution & branch paradox
Mobile-first transformation
Mobile banking has evolved from convenience to primary channel, with 3.6 billion global users. Africa leads with 600M+ mobile money users (M-Pesa, MTN), while developed markets show 85%+ app penetration. Mobile transactions now exceed branch and ATM combined, costing $0.10 versus $4 for branch transactions—enabling 15-20% cost-to-income ratio improvements with mobile-first operations. Mobile platforms generate real-time behavioral data enabling AI-driven personalization, fraud detection, and alternative credit scoring.
The branch paradox
Despite mobile dominance, branches remain strategically valuable but economically challenged. The paradox: customers demand branch access (trust, complex transactions) but rarely visit (2-3x annually versus 50x mobile logins). Branch costs average 60-70% of operating expenses while generating declining transaction volumes. Resolution strategies include right-sizing footprint 25-40% in mature markets, converting full branches to advisory centers focused on wealth management, deploying video banking kiosks in retail locations (60-75% cost reduction), and transforming flagship branches into innovation showcases. Regional variations persist: GCC and Asia maintain expansion in underbanked areas; Europe and North America focus on optimization; Africa bypasses branches entirely with mobile-first models.

Profitability drivers & banks vs. fintechs
Profitability framework
Banking profitability faces structural pressure from NII margin compression (US Declining, Europe stable), rising compliance costs (+25%), and fintech competition. Successful banks pivot to fee-based revenue while leveraging technology for cost reduction. Target metrics: ROE 10-12% (developed markets), 15-18% (emerging); cost-to-income <55% (world-class), 60-65% (acceptable); fee income 35-45% of total revenue (diversified), <25% (vulnerable).

Banks vs. fintechs: competition & collaboration
The global fintech ecosystem has matured from disruptive challenger to strategic partner within the $2.5 trillion global payments industry. Digital payment transaction value reached $18.7 trillion in 2024, projected to exceed $33.5 trillion by 2030. The fintech market itself was valued at $340 billion in 2024, forecast to reach $1.13 trillion by 2032 at a 16.2% CAGR.
The competitive narrative is evolving from displacement to ecosystem integration. Most successful fintechs partner with banks for regulatory compliance, capital, and customer trust, while banks leverage fintech innovation and agility.
Banks hold advantages in trust and regulation (established relationships, deposit insurance, regulatory expertise), scale and capital (deep balance sheets, deposit funding), and broad customer demographics.
Fintechs excel in technology (modern stack, cloud-native, rapid deployment), customer acquisition (digital-native millennials/Gen Z, niche focus), and lighter initial regulation enabling faster innovation.
Strategic response: Build internal fintech capabilities (digital banks, instant payments, robo-advisory); buy proven fintechs strategically (focus on technology and talent); partner through API-based collaborations (BaaS models growing 40% annually); compete in core deposit and lending franchises using superior pricing, service, and regulatory moats.
Culture transformation imperative
Technology and strategy fail without cultural alignment. Banking's traditional risk-averse, hierarchical culture conflicts with the speed, experimentation, and customer-centricity required for digital transformation. Successful banks systematically rebuild organizational culture around agility, innovation, and accountability.
Cultural pillars
• Speed over perfection: Move from waterfall to agile. Deploy AI features in weeks, not quarters. Accept 80% solutions that improve iteratively.
• Data-driven decisions: Replace HiPPO (Highest Paid Person's Opinion) with A/B testing and analytics. Empower analysts to challenge conventional wisdom.
• Customer obsession: Reorient from product-centric to customer journey-centric. Measure NPS, engagement, retention rigorously.
• Talent transformation: Recruit technologists and product managers aggressively. Retrain legacy workforce in digital skills. Accept higher tech compensation.
• Calculated risk-taking: Create innovation sandboxes where failure is acceptable. Fund 10 experiments knowing 7 will fail, but 3 might transform business.

Conclusion: The resilient bank of 2028
The banking landscape of 2026-2028 will be defined by institutions that successfully balance contradictory imperatives: maintaining branch presence while going mobile-first, competing with fintechs while partnering strategically, preserving risk culture while accelerating innovation, and defending profitability while investing heavily in transformation.
Regional strategies must adapt to local realities—from Africa's mobile money leapfrogging to GCC's mega-project financing to developed markets' fee income pivots—yet all share common foundations: data excellence, cultural agility, customer obsession, and operational efficiency. The profitability equation is clear: NII will decline in most markets, requiring 40%+ fee income ratios. Cost-to-income must reach sub-55% through AI automation and branch rationalization. Mobile transactions must exceed 75% of total volume.
Critical success factors

The strategic Mandate:
Transform technology, operations, and culture simultaneously. No dimension succeeds in isolation. Build mobile-first experiences rivaling fintechs. Rationalize physical infrastructure while preserving strategic presence. Cultivate innovation culture within risk management frameworks. Diversify revenue while controlling costs. Partner with fintechs where strategic, compete where necessary, and maintain customer trust as the ultimate competitive advantage. Deploy capital efficiently to modernize infrastructure, achieve regulatory excellence, and scale AI from pilots to enterprise-wide drivers.

Leverage community expertise to redefine finance
Our communities cover diverse topics such as digital transformation, SME finance, or Embedded insurance, providing a platform to learn from industry experts and peers.